UMTS in general
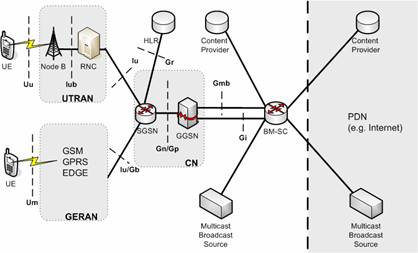
UMTS network is split in two main domains: the User Equipment (UE) domain and the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) domain. The UE domain consists of the equipment employed by the user to access the UMTS services. The PLMN domain consists of two land-based infrastructures: the Core Network (CN) and the UTRAN. The CN is responsible for switching/routing voice and data connections, while the UTRAN handles all radio-related functionalities. The CN is logically divided into two service domains: the Circuit-Switched (CS) service domain and the Packet-Switched (PS) service domain. The CS domain handles the voice-related traffic, while the PS domain handles the packet transfer.
The PS portion of the CN in UMTS consists of two kinds of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Support Nodes (GSNs), namely Gateway GSN (GGSN) and Serving GSN (SGSN). SGSN is the centerpiece of the PS domain. It provides routing functionality interacts with databases (like Home Location Register (HLR)) and manages many Radio Network Controllers (RNCs). SGSN is connected to GGSN via the Gn interface and to RNCs via the Iu interface. GGSN provides the interconnection of UMTS network (through the Broadcast Multicast-Service Center) with other Packet Data Networks (PDNs) like the Internet.
UTRAN consists of two kinds of nodes: the first is the RNC and the second is the Node B. Node B constitutes the base station and provides radio coverage to one or more cells. Node B is connected to the User Equipment (UE) via the Uu interface (based on the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access, WCDMA technology) and to the RNC via the Iub interface.
Regarding the transmission of the packets over the Iub and Uu interfaces, it may be performed on common (i.e. FACH), dedicated (i.e. DCH) or shared (i.e. HS-DSCH) transport channels.